A stress echocardiogram is usually done on low cardiac risk patients with unexplained chest pain or dyspnoea, which has been triggered by physical activity.
Non pharmacological stress echocardiogram
This is an echocardiogram carried out during, or just after, a period of exercise on a treadmill or exercise bike, usually to assess mitral or aortic valve function, or assess left ventricular outflow tract velocities if hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is suspected.
Pharmacological Stress Echo
For those patients who may have had unequivocal result from a non pharmalogical stress echo or may be physically be unable to do one, a pharmalogical stress echo may be carried out. A pharmalogical echo may also be used in patients with known coronary artery disease and left ventricular dysfunction, to help identify whether intervention to the arteries might help heart function (viability study). Similarly, in patients who have aortic stenosis and left ventricular impairment, a low-dose dobutamine study can help us decide how severe the aortic stenosis actually is.
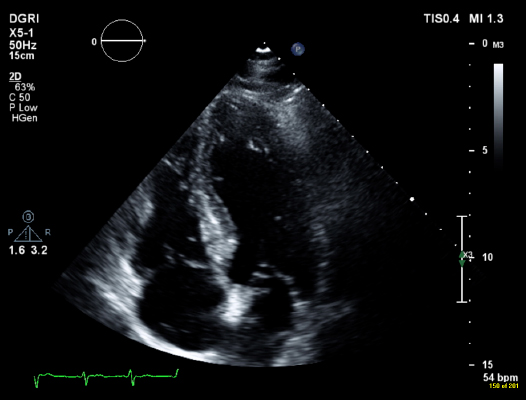
The test is used to visualise the effect of increasing heart rate on the contraction of the left ventricle and determine whether there is reduced blood flow to the myocardium, producing ischaemic changes on the scan and ECG.
A Dobutamine infusion (or occasionally Dipyridamole depending on information required) is used to artificially increase the heart rate. An echo is then performed at pre determined stages. This is usually pre Dobutamine; at low dose; peak heart rate; and in recovery stage.
The test involves the patient being cannulated and attached to an injection pump containing a saline/ Dobutamine mix. 12 lead ECG and BP are continuously monitored throughout the test.
- Benefits:
- Instant results
- Risks:
- Hypotension
- Arrythmia: AF, VT
- Chest pain: causing ischaemia or M.I
Dobutamine Stress Echo (DSE) is generally done within a specialised department, with appropriate resuscitation equipment and medications close at hand. A specialist nurse, cardiologist and echo physiologist are present throughout.
The infusion is run until the desired heart rate is reached. This is the same as an Exercise Tolerence Test (ETT). It is calculated as 220 beats per min (minus) – the patients age, x 0.85%. Atropine may be added if the heart rate response is inadequate.
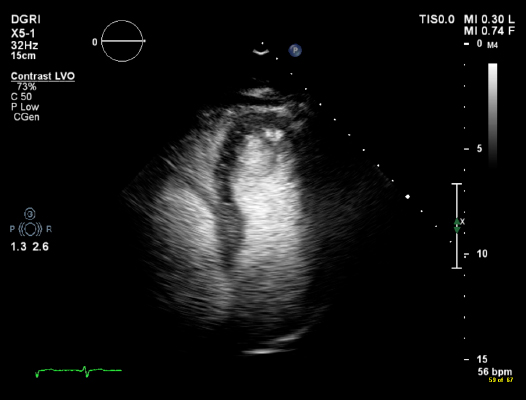
A special contrast agent containing microbubbles of sulphur hexafluoride is injected to enhance the echo images by defining and outlining the LV cavity and myocardium. Sonovue contrast is the most commonly used contrast agent in the UK. This gas has a very short life and is absorbed by the lungs very quickly, and has no effect on the patient.
The full test lasts approximately 40 minutes and the results accurately analysed.
Same image with contrast medium
Page last reviewed: 30 Jul 2020


