Gene testing can find:
- Pathogenic mutations. Other family members can then be offered a gene test.
- A variant of uncertain clinical significance (VUS). Uncertainty about a VUS result makes a VUS unreliable for diagnosis and this is only used in selected, individual cases.
- No mutation, therefore, cannot offer a gene test and will not be useful to test other family members.
Genetic testing may:
- provide confirmation of a familial diagnosis
- if a pathogenetic mutation is found, can offer predictive testing for close relatives
- guide discussion around reproductive options
- guide treatment options
- help predict the likely severity of the condition
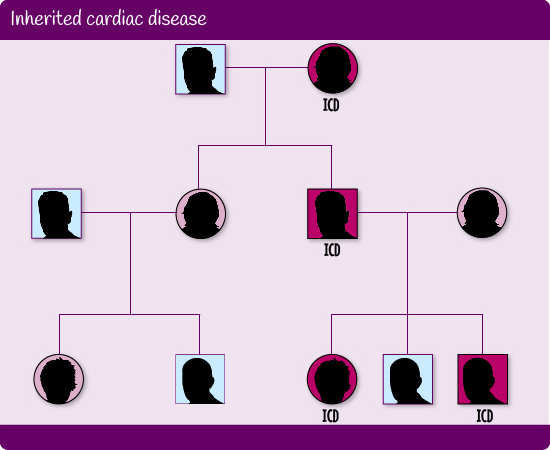
Cascade (predictive) screening involves testing close relatives of patients diagnosed with inherited cardiac disease, or of a Sudden Cardiac Death victim, by cardiac and genetic assessment. Cascade screening achieves a greater rate of diagnosis than general population screening. Once a diagnosis is confirmed in an individual, testing is extended to first degree and second degree relatives. If relatives test positive, their first and second degree relatives are approached and offered testing, and so on.
Benefits of cascade screening include:
- exclusion of causative mutation in at risk family members – no further clinical screening required if negative gene test
- early detection and treatment of inherited heart disease if found to be mutation positive
- removes continuous uncertainty about whether or not an individual will develop the condition
- can resume “normal” lifestyle if negative for mutation, for example, intensive sport training
- result may guide on-going frequency of of screening/cardiac follow up required
- opportunity to adapt lifestyle if positive for mutation
Pulse point
Although genetic testing has numerous benefits, it does have limitations:
-
- it does not address whether the person will show symptoms of the disorder, the likely severity of the problem or how it may develop and progress
- there may be a lack of treatment available for condition detected, causing psychological anxiety
- some prophylactic treatment options may improve outcomes for individuals at risk but some of these are not yet proven
- testing does not exclude a genetic cause (in cases of an unknown gene)


