
Katie attends the paediatric cardiology clinic for assessment, where it is diagnosed that her unborn baby has severe Tetralogy of Fallot (ToF). The condition is explained to the parents, prior to Katie meeting with the consultant obstetrician to discuss the implications of this for her pregnancy.
What is Tetralogy of Fallot?
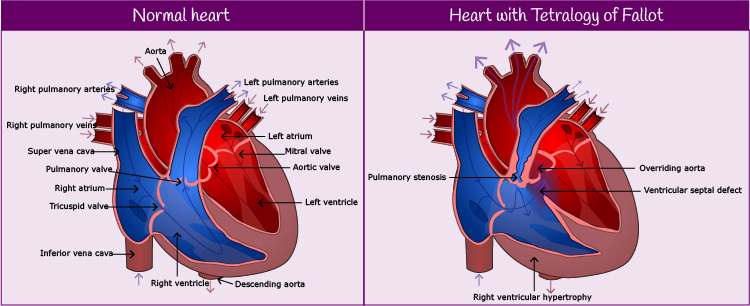
ToF is one of the most common forms of cyanotic congenital heart disease and requires surgical intervention once the baby is born. ToF is made up of four features:
- a ventricular septal defect
- an overriding aorta (taken with a ventricular septal defect, this causes oxygenated and non-oxygenated blood to mix)
- pulmonary stenosis
- right ventricular hypertrophy (results from the pulmonary stenosis)
Pulse point
ToF can cause problems in adulthood. These include:
- pulmonary regurgitation
- right ventricular dilation – secondary to severy pulmonary regurgitation
- residual RVOTO (Right Ventricular Outflow Tract Obstruction) residual obstruction at the level of the pulmonary valve and/or artery)
- residual ventricular septal defect – may be due to patch dehiscence after surgical repair
- aortic regurgitation leading to left ventricular dysfunction
- arrhythmia – occurs in approximately 33% of patients
- Sudden Cardiac Death – occurs in approximately 0.5-6% of patients


