A combination of:
- New, higher cerebral dysfunction (such as aphasia, inattention, dyspraxia, agnosia)
- Homonymous visuospatial field deficit
- Weakness or sensory loss involving at least 2 of 3 parts of the body (face, arm, leg)
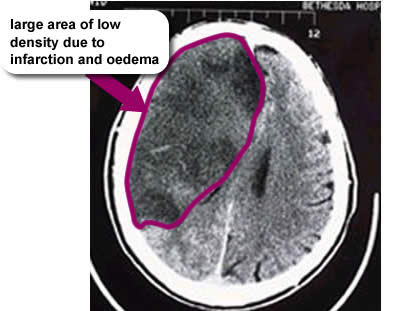
Predicted outcomes at 30 days post-TACI:
- 40% of patients dead
- 56% of patients dependent
- 4% of patients independent
(Reference: Bamford, J., Sandercock, P., Dennis, M., Burn, J. and Warlow, C.1991. Classification and natural history of clinically identifiable subtypes of cerebral infarction. Lancet, 337 pp. 1521-1526.)
Mr McTavish was transferred to the stroke unit at his local hospital in Scotland, where the following physical assessment took place.
Page last reviewed: 17 Feb 2020


