Your aim is to reduce the impact of Connie’s main risk factors which are:
- Impaired swallow
- High risk of malnutrition
The importance of involving patients and carers in these areas will also be addressed.
Your aim is to reduce the impact of Connie’s main risk factors which are:
The importance of involving patients and carers in these areas will also be addressed.
You have completed Connie’s early assessment. Here is a summary of the main outcomes:

From this summary is it apparent that we need to address Connie’s nutritional needs with some urgency. She is at high nutritional risk as her MUST Score is 5. As she is NBM, the Speech and Language Therapist will undertake a full swallowing assessment later today which will help to determine to the most suitable options for nutrition support?
Referrals have also been made to the Dietitian and Pharmacist.
Having identified the risks you can now go on to manage the risks.
Connie is presently NBM, we don’t know how long this will continue, therefore at present she needs to be scored appropriately.
Step 3 – Acute disease state- so likely nil intake: score as 2
Step 1- BMI = 18 score MUST = 2
Step 2 – weight loss 6.5% MUST = 1
Step 3- NBM MUST = 2
Total MUST score = 5
Refer to your local protocol but a MUST score above 2 usually indicates increased nutritional risk and a referral to dietetics should occur at this point.
Considering Connie’s reported unplanned, weight loss, what does she score for step 2 of the MUST tool?
(Reminder: Connie was 8 stone 2lbs (51.7kg) for the last 3 years. She is now 7 stone 7lb (47.6kg). She has lost 9lb (4.1kg).).
Use the example weight loss score chart to work out Connie’s weight loss over a 3-6 month period:
BAPEN Step 2 BMI Weight Loss Score (PDF)
Connie’s weight loss is 7.9% – is this significant?
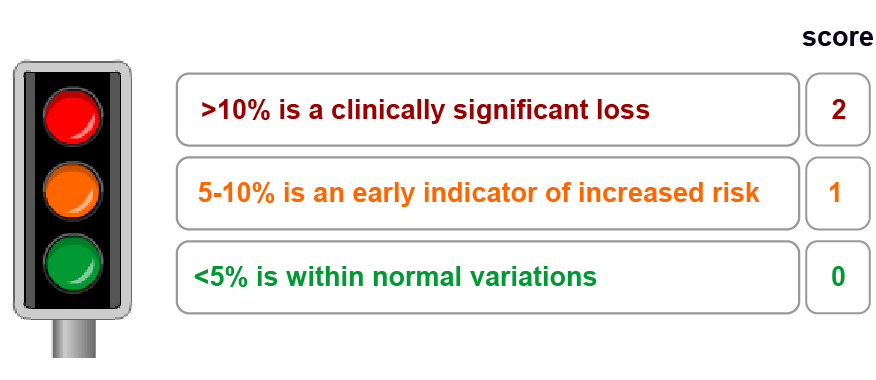
Connie scores 1– unintentional weight loss can be a sign of malnutrition, whereby your body is not receiving the correct amount of nutrition either due to reduced intake, increased losses or increased needs.
Connie is too drowsy to tell you about her weight at present. You ask Connie’s daughter for more information and she tells you she thinks her mum is about 5’4” tall (1.63m) and that she lost some weight. You have checked Connie’s weight on the ward and she is 7 stone 7lb (47.6kg).
STEP 1 – BMI
Use the link below to calculate Connie’s BMI
https://www.bapen.org.uk/pdfs/must/bmi-weight-loss-charts/must-table-up-to-100kg.pdf
Using Connie’s BMI, determine her score for step 1 of MUST tool
BMI >20 (>30 Obese) = Score 0
BMI 18.5-20 = Score 1
BMI <18.5 = Score 2
|
ft
in
lbs
cm
kg
BMI |
Malnutrition and more specifically in this instance undernutrition affects every system in the body resulting in increased vulnerability to illness and increased complications. Malnutrition is not easily recognised in the early stages, particularly in patients that are overweight or obese.
Although often identified in hospital, malnutrition usually starts in the community:
Hence the need for appropriate screening techniques.
All hospital patients on admission should be screened for risk of malnutrition on admission and at least weekly thereafter (RCP 2016). Screening should be repeated weekly for inpatients as set out in NICE clinical guideline 32 recommendation 1.2.6
Connie is new in the ward – her clothes and jewellery are loose and she appears to be frail, which may suggest she had lost some weight prior to her admission to hospital. She is currently nil by mouth (NBM) so it is important to establish her nutritional risk.
You should also speak with her daughter to gather some more background information as Connie is fatigued and has difficulty answering your questions at present.
In order to calculate Connie’s nutritional risk you need to consider the following 3 aspects:
When a patient is NBM it is important to consider how medications can be administered in consultation with the pharmacist and medical staff.
As Connie is NBM this would indicate that an NG tube should be passed. However, the Speech and Language Therapist will assess her swallowing ability later today. The decision to pass an NG tube will be made following this assessment.
On each exercise click the ‘Check‘ button after you make your selection and then > to continue:
Hydration is essential to life, and deprivation can have life-threatening consequences within hours. Fluid status in acute illness needs to be closely monitored.