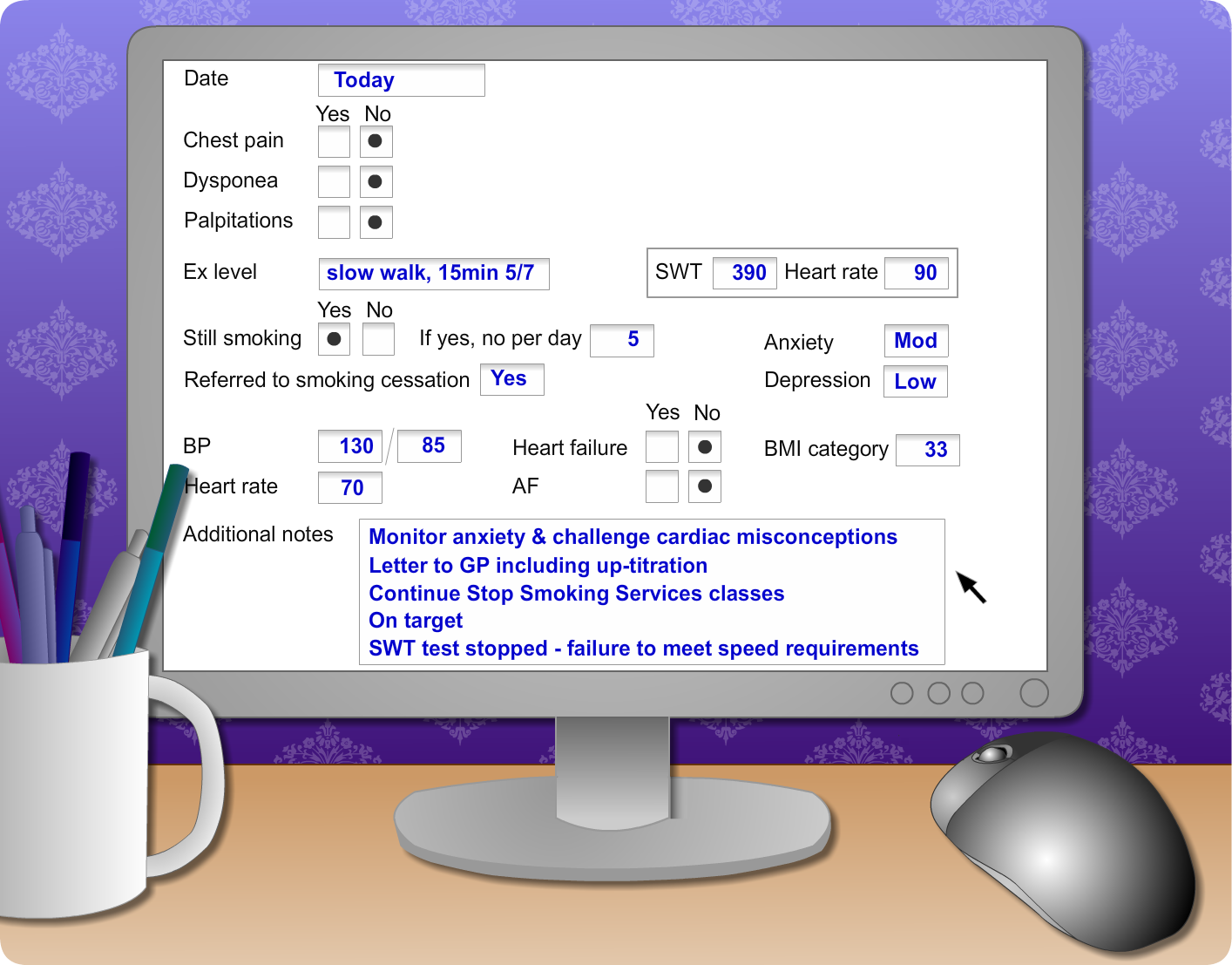
John attends his out-patient cardiac rehabilitation follow up. Look over Johns results on the screen to see the changes he has made in the goals he set during the agenda setting session.
John’s anxiety and depression scores will have been achieved when he is assessed using a validated mental health screening tool. He was not found to be severely anxious but if he was he would have been referred to a psychology service. Referral and access will vary from area to area.
Date: Today
- Chest pain: No
- Dysponea: No
- Palpitations: No
- Ex level: slow walk, 15min 5/7
- SWT: 390metres
- Heart rate: 90bpm
- Still smoking: Yes
- If yes, no. per day: 5
- Referred to smoking cessation: Yes
- Anxiety: Mod
- Depression: Low
- BP: 130/85
- Heart rate: 70
- Heart failure: No
- AF: No
- BMI category: 33
- Additional notes:
- Monitor anxiety & challenge cardiac misconceptions
- Letter to GP including up-titration
- Continue smoking cessation classes
- On target
- SWT test stopped – failure to meet speed requirements of test
Pulse point
Prior to entry into a cardiac rehabilitation exercise programme, all patients should be risk stratified as low, moderate or high risk and undergo a functional capacity test. Risk stratification is an algorithm used to establish risk of cardiac events (AACVPR). The tool allows health professions to individualise the prescription of exercise and identify the need and extent of supervision required. There are various tests of functional capacity used in cardiac rehabilitation . The Shuttle Walk Test (SWT) is commonly used and assists exercise prescription and can be used to evaluate progress in the cardiac rehabilitation programme.
Page last reviewed: 27 Jul 2020


