Before continuing with the atrial fibrillation module we recommend that you complete the learning outcomes and assessment of module 1: Healthy Heart & Investigations. You should pay particular attention to the pages relating to normal cardiac conduction pathways.
In people with AF the left atrial appendage which sits adjacent to the left atrium, is clinically important. Have a look at more detailed physiology in the picture below. In AF the development of thrombus usually takes place in the left atrial appendage due to its position.
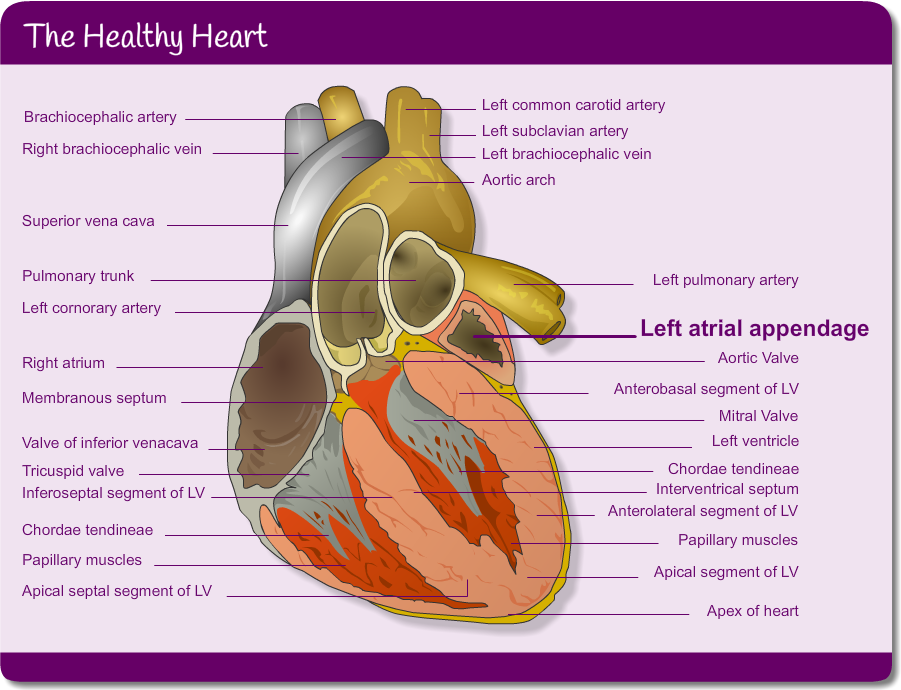
The healthy heart
Labels:
- Brachiocephalic artery
- Right brachiocephalic vein
- Superior vena cava
- Pulmonary trunk
- Left cornorary artery
- Right atrium
- Membranous septum
- Valve of inferior venacava
- Tricuspid valve
- Inferoseptal segment of LV
- Chordae tendineae
- Papillary muscles
- Apical septal segment of LV
- Left common carotid artery
- Left subclavian artery
- Left brachiocephalic vein
- Aortic arch
- Left pulmonary artery
- Left atrial appendage
- Aortic Valve
- Anterobasal segment of LV
- Mitral Valve
- Left ventricle
- Chordae tendineae
- Interventrical septum
- Anterolateral segment of LV
- Papillary muscles
- Apical segment of LV
- Apex of heart
Pulse point
These extra resources may be useful for your learning around Atrial Fibrillation:
Atrial Fibrillation Video
Page last reviewed: 29 Jul 2020


