What is an EP study?
An electrophysiology study or EP study is a minimally invasive procedure which aims to map the electrical conduction system of the heart with the aim of identifying the causes of arrhythmias. By identifying the location of the patient’s arrhythmia, a treatment plan can be formulated.
An EP Study is often an elective procedure carried out in a specialist Cardiac Catheter Laboratory in a hospital. It usually requires the patient to stay for one night in hospital. It is carried out by a team including a cardiologist, cardiac physiologists, radiographers and nurses.
The Cardiac Catheter Lab layout will differ between hospitals. The X Ray machine usually arches over the patient and can provide images of the heart and the catheter placements during the procedure.
The EP Study:
- may take around 2-3 hours and sometimes longer
- The patient will be taken to the Cardiac Catheter Lab and made as comfortable as possible on an X Ray table
- At the start of the procedure the patient will often be offered a sedative through an IV cannula to help them relax
- Once comfortable and medication administered, the team will then start connecting the patient to monitoring equipment
The cardiologist and cardiac physiologists may already have knowledge of the patient’s arrhythmia which will dictate the equipment used during the procedure. Standard monitoring equipment will be applied such as BP cuff, SpO2 probe and 3 lead ECG. If appropriate, defibrillation pads may be connected at the start of the procedure if the patient’s arrhythmia is know to be unstable/life threatening.
A local anaesthetic will be injected at the catheter entry sites. The entry sites are usually at the right groin and right wrist to gain access to the right femoral vein and the right radial artery or a vein in the right forearm.
The cardiologist will start the procedure and ‘map’ a picture of the heart and electrical conduction system using the catheters. The X Ray machine allows the cardiologist to locate the chambers of the heart
Below are two examples of diagnostic catheters. As you can see they are very flexible and have electrodes along the outside and on the tip:
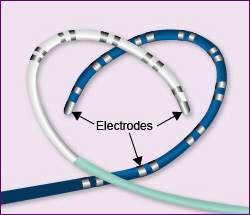
There may be 3 to 5 catheters used during a procedure. The catheters send data to the cardiac physiologists and it is interpreted in graphics an ECG waveforms for the cardiologist. The electrodes on the catheters can detect the electrical activity in the heart. When an arrhythmia is detected the cardiologist can see where it is present and can make a treatment plan from there.
During the procedure, the cardiologist may identify an arrhythmia which can be treated with ablation therapy, where radiofrequency energy is used to destroy or freeze the particular area of heart tissue that is the source of the arrhythmia. Arrhythmias which can be treated by ablation are:
- Supra-ventricular tachycardia
- Wolff Parkinson White
- Atrial Flutter
- Atrial Fibrillation
- Atrial Tachycardia
- Ventricular Tachycardia
It is essential that emergency resuscitation equipment is readily available during this procedure due to the arrhythmias which may be precipitated by the test.
Other treatment options following an Electrophysiology Study include medication therapy, a pacemaker, an implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) or cardiac surgery.
See Additional Information for a BHF patient video.
Well done, you have reached the end of this section.
What do you want to do next?
- Restart this section
- Select a new section
- Leave feedback
Page last reviewed: 31 Jul 2020


